The Ultimate Guide to Laser Engrave Metal: Precision, Power, and Performance
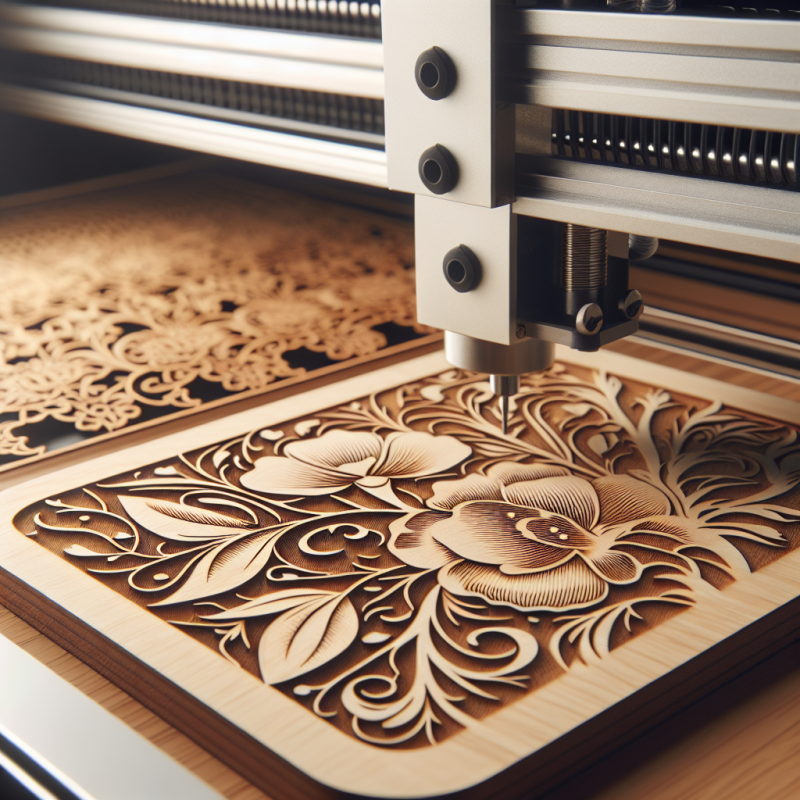
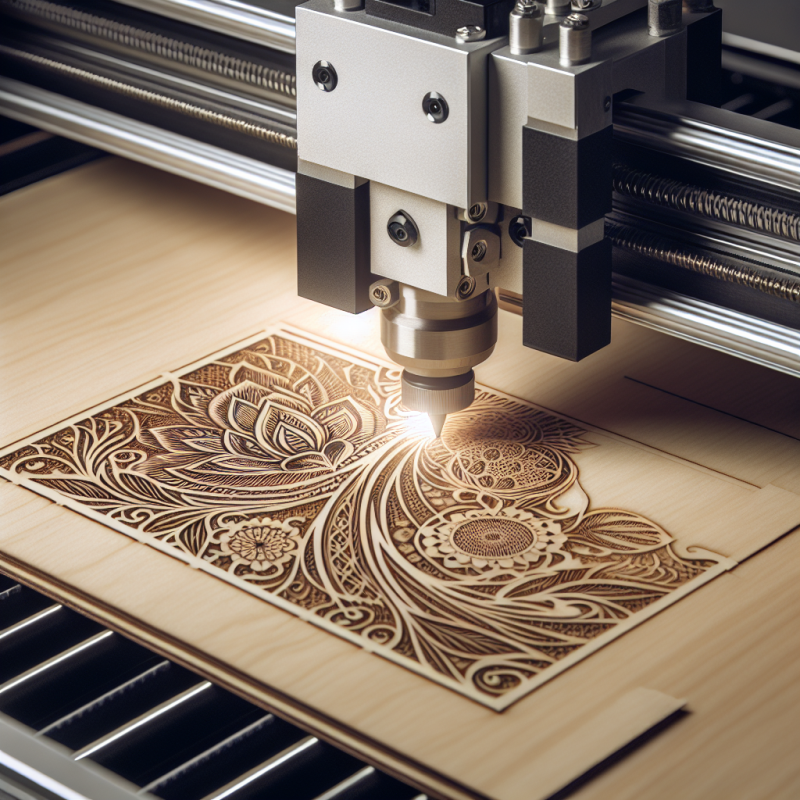
In the world of modern manufacturing and creative design, laser engrave metal has emerged as a game-changing technology. Whether you’re crafting custom jewelry, industrial components, or artistic pieces, laser engraving machines offer unmatched precision and versatility. But what makes these machines so revolutionary? Let’s dive into the mechanics, applications, and benefits of laser engrave metal technology.
How Do Laser Engraving Machines Work?
At their core, laser engrave metal systems use focused laser beams to vaporize or alter the surface of metallic materials. The process involves three key steps:
- Beam Generation: A high-intensity laser (fiber, CO2, or diode) produces concentrated light energy.
- Material Interaction: The laser beam removes microscopic layers of the metal surface, creating permanent marks.
- Control System: Advanced software guides the laser’s path, ensuring intricate designs are replicated accurately.
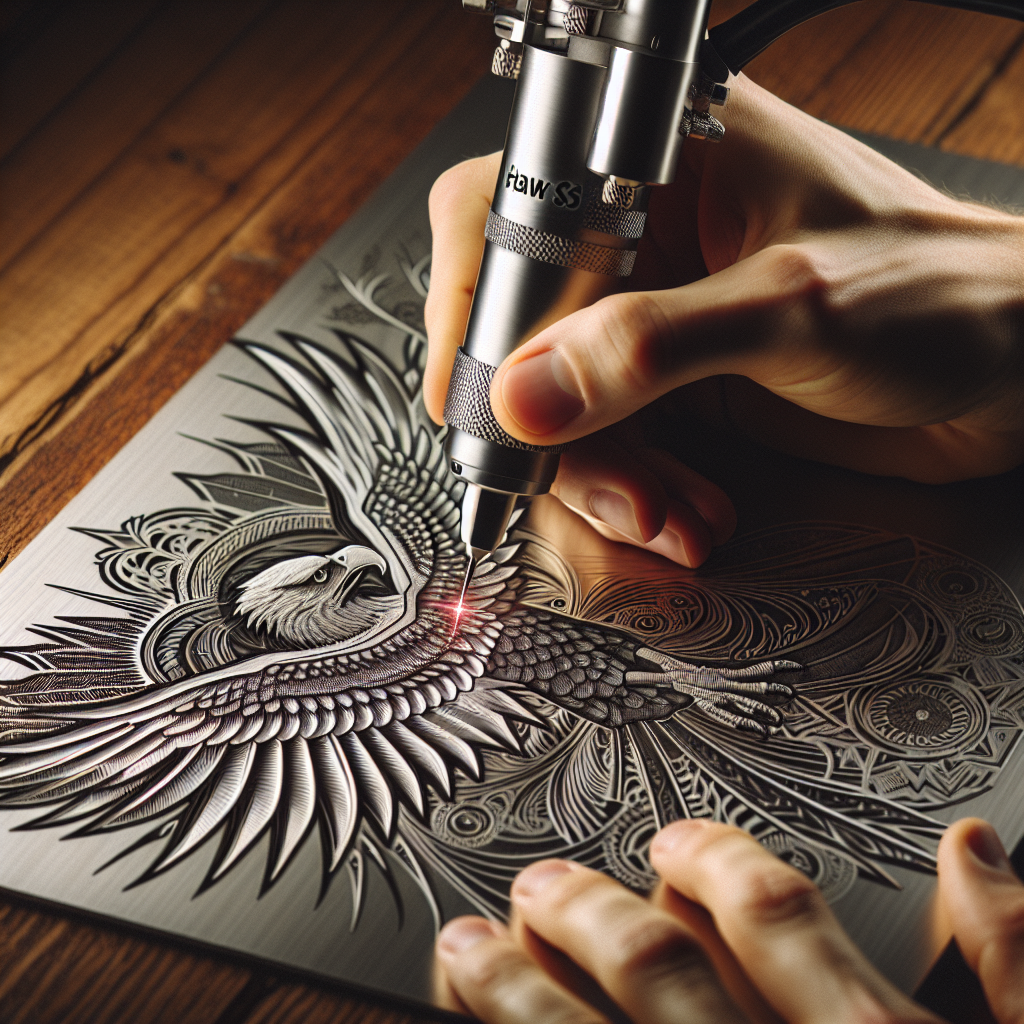
For instance, the Hawk S1 Laser Engraving Gun utilizes a fiber laser optimized for metals like stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium. Its precision is measured in microns, making it ideal for industrial-grade applications. Did you know? Some systems can achieve speeds of up to 7,000 mm/s without compromising detail.
Why Choose Laser Engraving Over Traditional Methods?
Traditional engraving techniques, such as mechanical etching or chemical processes, often struggle with consistency and scalability. In contrast, laser engrave metal machines provide:
- Superior Precision: Achieve complex geometries and fine details impossible with manual tools.
- Non-Contact Process: Minimizes material distortion and tool wear.
- Speed: Complete projects in minutes instead of hours.
- Eco-Friendliness: No harmful chemicals or waste byproducts.
For businesses, this translates to lower operational costs and higher customer satisfaction. Imagine producing 500 custom-engraved metal plaques in a single day—this is the power of laser technology.
Applications of Metal Laser Engraving Machines
The ability to laser engrave metal opens doors across industries. Here are some standout examples:
- Aerospace: Engraving serial numbers on turbine blades for traceability.
- Medical Devices: Marking surgical tools with permanent identifiers.
- Automotive: Customizing car parts or creating branded emblems.
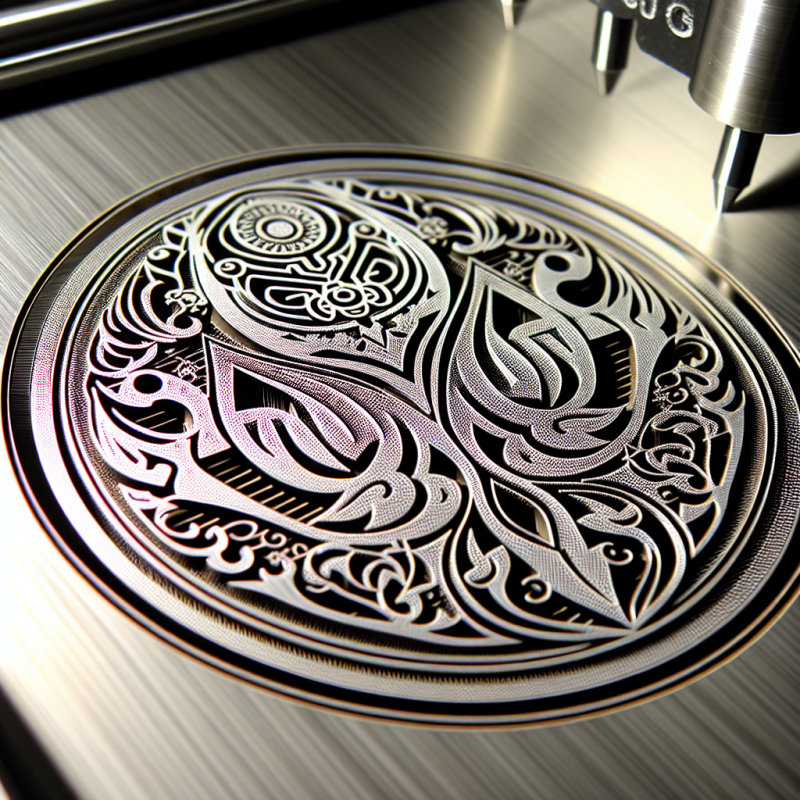
- Art and Jewelry: Designing intricate patterns on precious metals.
Question: Could your business benefit from integrating laser engraving into its workflow? The answer is likely yes—especially if durability and aesthetics matter.
Key Features to Look for in a Laser Engrave Metal Machine
Not all laser engravers are created equal. When selecting a system, prioritize these features:
- Laser Type: Fiber lasers excel on metals, while CO2 lasers are better for non-metals.
- Power Output: Higher wattage (e.g., 50W–100W) ensures faster engraving on tough alloys.
- Software Compatibility: Look for user-friendly interfaces that support vector files and 3D designs.
- Safety Mechanisms: Automatic shutoff, protective enclosures, and ventilation systems.
The Hawk S1, for example, combines a 60W fiber laser with intuitive software, making it a top choice for both beginners and experts. Pro Tip: Always test the machine on sample materials before committing to a purchase.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Metal Laser Engraving
While laser engrave metal technology is powerful, users may encounter issues like:
- Reflective Surfaces: Metals like copper or brass can reflect laser beams, reducing efficiency. Solution: Use anti-reflective coatings or adjust laser settings.
- Heat Distortion: Excessive power can warp thin materials. Solution: Optimize speed and pulse frequency.
- Inconsistent Depth: Uneven surfaces may cause variations. Solution: Use autofocus systems or rotary attachments.
Question: Are you prepared to troubleshoot these challenges, or would you prefer a plug-and-play solution like the Hawk S1?
Maintenance Tips for Long-Lasting Performance
To keep your laser engrave metal machine in peak condition:
- Clean lenses and mirrors weekly to prevent debris buildup.
- Check alignment regularly to ensure beam accuracy.
- Replace consumables (e.g., nozzles, filters) as recommended.
- Update software to access the latest features and bug fixes.
Neglecting maintenance can lead to costly downtime, so establish a routine inspection schedule. The Hawk S1 includes self-diagnostic tools to simplify this process.
Future Trends in Metal Laser Engraving Technology
The future of laser engrave metal systems is bright, with advancements like:
- AI-Driven Automation: Machines that self-adjust parameters based on material feedback.
- Hybrid Systems: Combining engraving with cutting or 3D printing capabilities.
- Green Lasers: Enhanced precision for ultra-fine details on sensitive metals.
Question: How will your business adapt to these innovations? Staying ahead requires investing in adaptable equipment like the Hawk S1, which is designed for future upgrades.
Conclusion: Why Invest in a Laser Engrave Metal Machine?
From boosting productivity to enabling creative freedom, laser engrave metal technology is a transformative tool. Whether you’re a small workshop or a large manufacturer, the right machine—like the Hawk S1—can elevate your capabilities and set you apart from competitors. Ready to take the leap? Explore how laser engraving can revolutionize your projects today.
Final Question: What’s stopping you from integrating the precision of laser engraving into your workflow? With machines becoming more accessible and user-friendly, there’s never been a better time to invest.